Patient-specific neural networks for autosegmentation and dose accumulation in abdominal MRI-guided radiotherapy
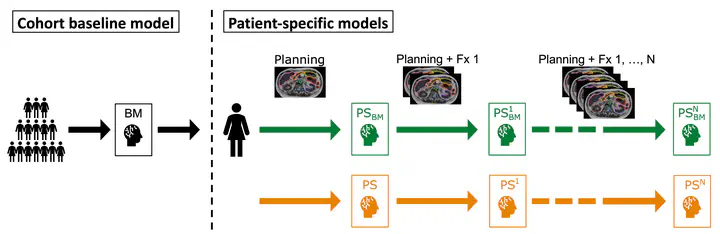 Approaches to patient-specific autosegmentation.
Approaches to patient-specific autosegmentation.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided online adaptive radiotherapy enables highly precise treatment of cancer patients. The dose to be applied for each treatment fraction is adapted to the patient’s anatomy on a daily basis. However, this significantly increases the complexity of the clinical workflow and treatment times. Particularly critical points are the lengthy daily recontouring of the fraction images and the precise tracking of the total dose applied over the course of fractionated adaptive radiotherapy.
While we addressed both points in the context of prostate cancer during the initial funding period (project number 2019.162.1), the current follow-up application (2019.162.2) aims at extending the developed methods to abdominal lesions and to complement them with novel approaches. First, patient-specific neural networks are to be implemented using expert contours from the initial planning phase for the autosegmentation of target and risk structures on fraction images. These will then be used to reconstruct the actual dose applied during fractionated MRI-guided online adaptive radiotherapy, taking into account all interfractional anatomical changes.
